Work Function
Work Function: Overview
In this topic, we will have a detailed view on nuclear reactors with their process of generation of electricity. It also discusses the fundamental parts required for a nuclear reactor and work function.
Important Questions on Work Function
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
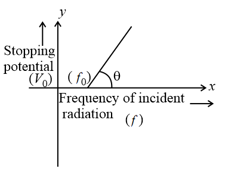
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
The difference between threshold wavelengths for two metal surfaces and having work function and in is:
{Given, }
The light emitted in the transition to (where is the principal quantum number of the state) in hydrogen is called -light. Find the maximum work function that a metal can have so that -light can emit photoelectrons from it.
The metal which has the highest work function in the following is
If the threshold wavelength for photoelectric effect on sodium metal is then find its work function.
Which of those metal having least work function among them?
In another experiment, a source of constant intensity and variable frequency is incident on a metallic surface. The graph shows the variation of the stopping potential with photon frequency , for a particular value of intensity.
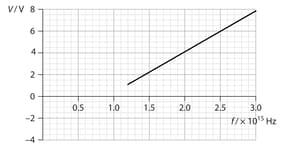
Use the graph to estimate the Planck constant obtained from this experiment.
In another experiment, a source of constant intensity and variable frequency is incident on a metallic surface. The graph shows the variation of the stopping potential with photon frequency , for a particular value of intensity.

Use the graph to estimate the work function of the metallic surface.
The charge of an electron was discovered by
Charge of an electron is
The work function of Platinum is twice that of Calcium. If the minimum photon energy required to emit photoelectrons from the surface of Platinum is then for Calcium, the minimum photon energy would be
Photoemission, thermionic emission, and field emission are the three basic processes that can emit electrons from a material surface.
The phenomenon of electron emission is defined as the emission of electrons from the surface that is caused by a change in temperature, radiation, or a strong electric field.
The electrons which escape the nuclear force, cannot come out of the surface of the conductor.
Electrons which cannot escape from the nuclear force are called free charges.
Differentiate between free charges and bound charges.
Free charges cannot conduct electricity.
Inner electrons which can escape from the nuclear force are called bound charges.
Bound charges cannot conduct electricity.
The work function of a substance is . The longest wavelength of light that can cause photoelectron emission from this substance is approximately
